Hyaluronic Acid is intended for use in nutritional supplements to improve joint and skin health and in cosmetics to increase skin hydration and reduce wrinkles.
|
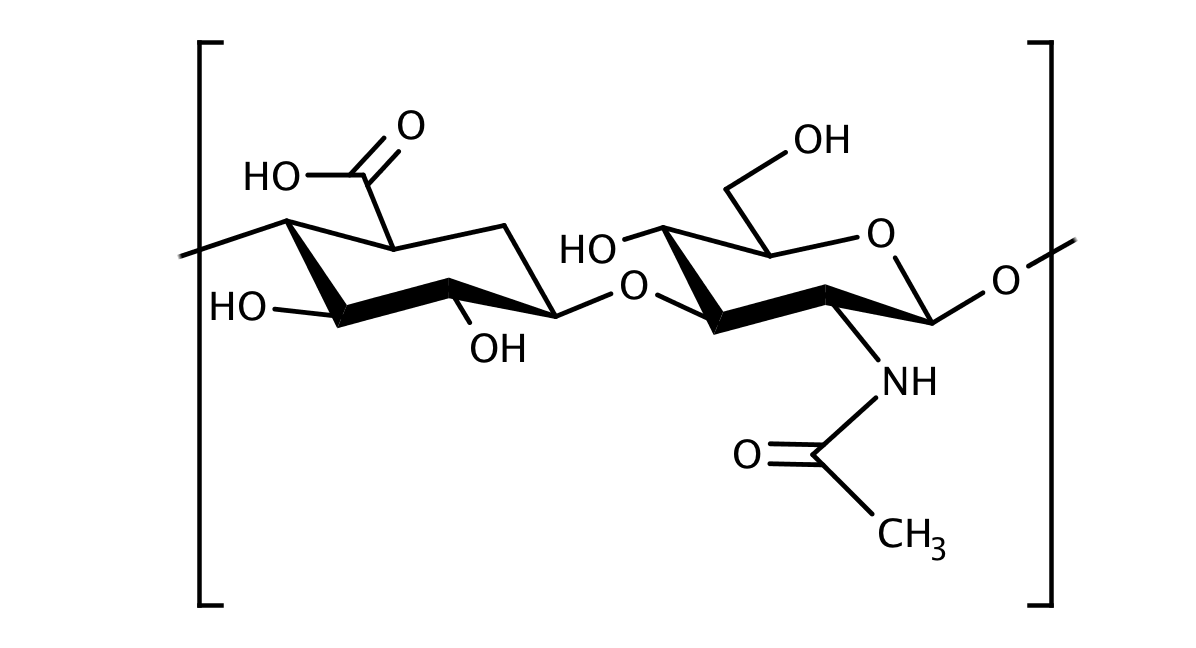
| Hyaluronic Acid structure |
Also called hyaluronan, Hyaluronic Acid is a natural polymer consisting of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine monomers. It belongs, together with substances like chondroitin sulphate, to the group of glycosamino-glycans (GAGs). Hyaluronic Acid can hold water molecules up to 1000-fold of its own weight and is present in many body tissues, primarily in the extracellular matrix, to bind water.
Physiological Function
In combination with collagen and elastin, it forms a supramolecular structure in the skin that increases skin stiffness. In this matrix structure, it improves skin hydration and can help to reduce wrinkles.
Additionally, in joints, Hyaluronic Acid forms part of an extracellular structure together with collagen and aggrecan. In the synovial fluid, it binds water and releases it under pressure. This gives a lubricating and cushioning effect to joints.
In other tissues, Hyaluronic Acid increases stiffness and pressure resistance. It also plays a role in diffusion processes in the interstitial space.
Different Types of Hyaluronic Acid
Our Hyaluronic Acid is manufactured from fermented plant sources. It is available as the salt form, sodium hyaluronate, in molecular weights from 3 kDa to 2 MDa. The larger types are more similar in their molecular weight to the natural form and are very efficient in binding water. On the other hand, they form high viscosity gels in water even at low concentrations, which makes them difficult to formulate. In addition, their absorption rate after oral or topical administration is low compared to low weight types.
Use in Cosmetics
Hyaluronic Acid, or respectively its sodium salt, is used in all types of care and colour cosmetics in concentrations of up to 2%. The high molecular weight types do not penetrate the skin but form a hydrated viscoelastic film on it. This process reduces transepidermal water loss (TEWL) without an occlusion effect. Low molecular weight types can penetrate the skin, where they increase moisture levels, help to repair damaged skin and can even reduce wrinkles. Hyaluronic Acid is often used in lipsticks, moisturizing face or body creams and lotions but also in mascara, makeup foundations and other colour cosmetics and rinse-off formulations.

Use in Nutritional Supplements
Orally, Hyaluronic Acid is used for both skin hydration and for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Since molecules with a molecular weight above 1 kDa are generally not absorbed from the intestine, it needs to be decomposed by enteric bacteria to oligosaccharides to be taken up systemically. Therefore, low molecular weight types are recommended for oral use. On the other hand, there are also reports that the native form of the acid (high molecular weight) acts as an anti-inflammatory via receptors on intestinal epithelial cells.
The daily dose for the treatment of osteoarthritis ranged in studies from 48 mg/ day to 240 mg/ day and the molecular weight used from < 5 kDa up to approx. 2.5 MDa.
For skin improvement, Hyaluronic Acid was administered in clinical studies with a similar range, between 37.5 mg/ day and 240 mg/ day and with molecular weights between 30 kDa and 2.5 MDa.
We offer Hyaluronic Acid with following molecular weights (MW):
|
|
Other molecular weights are available upon request.
| Packing | 1 kg or 5 kg aluminium-foil bag, 25 kg drum |
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Storage | At 2 to 8 °C, protected from light, heat and oxygen. |
| Specifications Cosmetic Grade | |
| Specifications Food Grade | |
| MSDS |


