Coenzyme Q10, also known as ubiquinone, ubidecarenone, or coenzyme Q, is a fat-soluble coenzyme present in most animal cells. It plays a key role in the electron transport chain of aerobic respiration, which generates and stores energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).

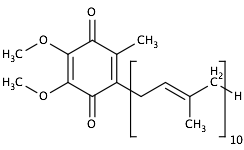 |
| Ubiquinone |
The body produces less and less Coenzyme Q10 with age, and low levels of Coenzyme Q10 have been found in patients with heart conditions, muscular disorders, and a broad variety of other maladies. Coenzyme Q10 is thought to help these diseases. Other conditions it has been used to treat include migraine, Down’s syndrome, Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, diabetes, and HIV/AIDS. It is taken to mitigate side effects of other medications, including chemotherapy. It may also help accelerate recovery from exercise.
Dosages and length of treatment vary widely. To improve exercise performance, 50-300 mg and as antioxidant, 60 - 150 mg of Coenzyme Q10 may be taken daily. To treat the side effects of chemotherapy a daily intake of 50 - 90 mg is recommended.
While a conclusive link is yet to be established, some studies have associated Coenzyme Q10 with symptom improvement in patients with coronary conditions. To treat chest pain, weakening of the heart muscle, high blood pressure, coronary heart disease, heart attack, heart failure, and other heart disorders, as well as to prevent heart disease, lower cholesterol or improve widening of blood vessels, daily doses from 30-600 mg have been recommended.

Coenzyme Q10 has been demonstrated to reduce wrinkles and improve aging in skin cells by reducing levels of cellular oxidation. For anti-aging purposes, a 1% Coenzyme Q10 topical cream may be applied.
We offer Coenzyme Q10 as powder with a concentration of 10% or 98%. Other concentrations are available upon request.
Packing and storage
| Packaging: | 1 kg container, 5 kg kg Al-foil bag or 20 kg/ 25 kg carton |
| Shelf life: | 2 years |
| Storage: | At ambient temperature, protected from light, heat and oxygen. |
Material Safety Data Sheet for Coenzyme Q10
|
| Coenzyme Q10 - MSDS |
|
| Coenzyme Q10 food - specification |
|
| Coenzyme Q10 pharma - specification |


